Introduction
1.4 What? (Spacecraft Definition)

A spacecraft is a “vehicle or device designed for travel or operation outside the Earth’s atmosphere” [Merriam-Webster]. Spacecraft are commonly separated into seven engineering subsystems (Structure, Attitude Determination & Control, Onboard Data Handling, Communication, Power, Thermal, Propulsion) and a Payload.

Structure & Mechanisms
-
- For large spacecraft, structures, mechanisms, and/or ordnance are often treated as separate subsystems.
- Provides structural support to spacecraft components and spacecraft configuration.
- Provides mechanical support for moving spacecraft elements (e.g., deploying and moving solar arrays, booms, or antennas).
- Provides ordnance for separating or deploying movable components (usually, ordnance is explosive in nature, e.g., explosive bolts)

Electrical Power Subsystem
-
- Supplies the spacecraft with the power required to sustain bus and payload operations.
- Provides excess power that may be stored (in batteries) for later use.
- All spacecraft must at least generate and distribute power.
- For most spacecraft that do not venture beyond the orbit of Mars, power generation is usually accomplished via solar cells.
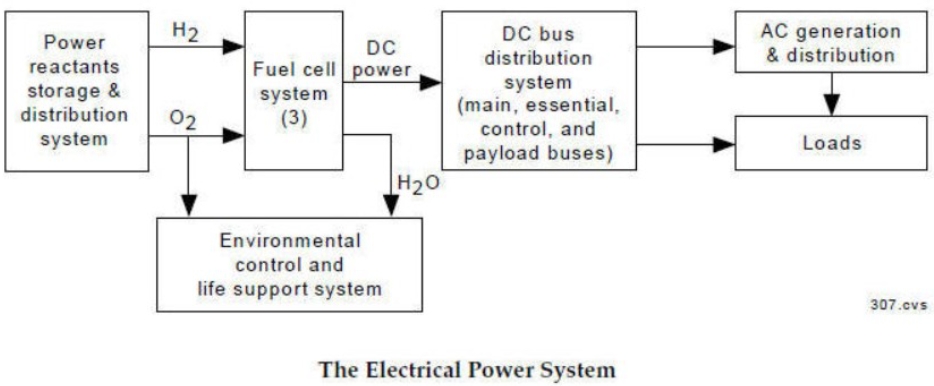
Space Shuttle Electrical Power System System Diagram. Image by Space Shuttle Guide.
Command, (Telemetry, &) Data Handling
-
- Receives, validates, decodes, and distributes commands to spacecraft systems.
- Gathers, processes, formats, and records spacecraft housekeeping telemetry and payload data for downlink and/or use by the onboard computer (OBC).
- All spacecraft must handle commands and data, even Sputnik, which had to send 1’s and 0’s across electronics to blink its light.

Communications/RF
-
- Receives command data transmitted from a ground/space-based communications antenna.
- Transmits telemetry data (containing spacecraft health and payload data) to ground/space-based receiving antennas.
- All spacecraft must communicate with its operators; Sputnik blinked lights to know it had survived in space.

Attitude, Determination, Control, and Sensing
-
- Senses changes in spacecraft orientation/stability.
- Controls spacecraft or component (e.g., antenna or sensor) orientation as required to support payload/spacecraft pointing requirements.

Thermal (Monitoring &) Control
-
- Maintains satellite components within required temperature limits by monitoring and heating/cooling components as required.

Propulsion
-
- Stores and converts the potential energy of onboard propellant(s) into the propulsive energy needed to exert a required force(s) on a satellite.

An example of architecture from the mid-2010s of a human spaceflight mission to Mars, as envisioned by the United States space agency by NASA. Image courtesy of NASA.
- Stores and converts the potential energy of onboard propellant(s) into the propulsive energy needed to exert a required force(s) on a satellite.
Environment Control & Life Support
-
- Provides control of the spacecraft environment to support humans and other required life forms by supplying oxygen, food, and potable water; maintaining comfortable temperatures; and removing, cleansing/ recycling waste products (gaseous, liquid & solid).
- Thermal Control is sometimes included in the ECLSS.




